Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.), a plant with both medicinal and aromatic values, its active components in the extract not only exhibit excellent antibacterial properties but also its potential in the fields of anti-inflammation and neuroprotection has increasingly attracted the attention of the scientific research community.
Inflammatory response is an important defense mechanism for the body to cope with damage, but chronic inflammation can induce various diseases; the high incidence of neurodegenerative diseases has also prompted researchers to continuously explore natural neuroprotective agents.
This article systematically expounds the dual biological activities of rosemary extract from five dimensions: active component analysis, anti-inflammatory mechanism, neuroprotective pathway, research data and application prospects, providing a scientific basis for its development in the field of medicine and health.
1. Core Active Components Mediating Anti-inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects
The anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects of rosemary extract originate from its complex chemical composition system, among which terpenoids and phenolic acid compounds are the main active carriers. These components exert their effects through different targets, and some components also have a synergistic effect, which together constitute the material basis of their biological activities. The functional positioning and characteristics of the core active components are shown in the following table:
| Active Component | Chemical Category | Main Biological Functions | Functional Characteristics |
| Rosmarinic Acid | Phenolic Acid | Potent anti-inflammation, scavenging free radicals, protecting nerve cells | Good water solubility, high bioavailability, significant dual advantages in anti-inflammation and neuroprotection |
| Carnosic Acid | Diterpene Acid | Inhibiting the release of inflammatory factors, activating neuroprotective pathways, antioxidant | Strong lipophilicity, easy to cross the blood-brain barrier, prominent targeting in neuroprotection |
| Carnosol | Diterpene Phenol | Regulating inflammatory signaling pathways, inhibiting neuronal apoptosis | High stability, able to regulate inflammation and nerve damage through multiple pathways |
| Ursolic Acid | Triterpenoid | Reducing inflammatory infiltration, promoting the repair of nerve cells | High safety, synergistically enhancing the neuroprotective effect with other components |
2. Anti-inflammatory Mechanism of Rosemary Extract: Multi-dimensional Regulation of Inflammatory Response
The occurrence and development of inflammatory response involve multiple links such as the release of inflammatory factors, activation of signaling pathways, and oxidative stress. Rosemary extract does not simply block a single link, but realizes the precise regulation of inflammatory response through a multi-dimensional model of “inhibiting pro-inflammatory factors – regulating signaling pathways – scavenging oxidative products”. Its core anti-inflammatory mechanism and action targets can be clearly presented through the following pathway diagram:
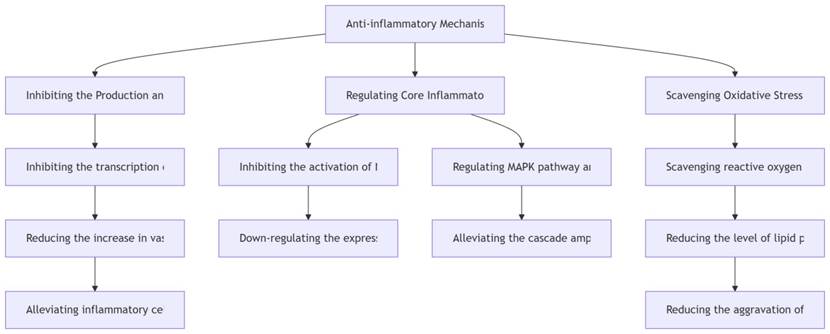
Studies have confirmed that rosmarinic acid has a significant inhibitory effect on the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced macrophage inflammation model. When the concentration of rosmarinic acid reaches 100μmol/L, the secretion of TNF-α and IL-6 decreases by 68.3% and 57.1% respectively. This effect is comparable to the inhibitory efficiency of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug ibuprofen (100μmol/L), but the risk of gastrointestinal irritation is significantly reduced. In addition, carnosic acid can reduce the joint swelling by 42.6% in the animal model of rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting the nuclear translocation of NF-κB, providing a new direction for the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases.
3. Neuroprotective Effect of Rosemary Extract: From Injury Defense to Functional Repair
The high metabolic rate and low regenerative capacity of nerve cells make them vulnerable to oxidative stress, inflammatory damage and accumulation of toxic substances, which in turn induce cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases. Rosemary extract exerts neuroprotective effects through a three-fold pathway of “defense – repair – regulation”. Its mechanism of action and related research data are as follows:
3.1 Core Neuroprotective Pathways
The active components in rosemary extract can cross the blood-brain barrier and act on the key links of nerve damage: first, scavenge reactive oxygen species in nerve cells through antioxidant effects to reduce oxidative stress damage; second, inhibit neuroinflammation and reduce the neurotoxicity caused by microglia activation; third, activate neuroprotective signaling pathways (such as Nrf2/ARE pathway) to promote the survival and repair of nerve cells; fourth, inhibit the aggregation of β-amyloid (Aβ) and reduce its toxic effect on nerve cells.
3.2 Key Research Data and Effect Evaluation
A number of animal experiments and in vitro cell experiments have confirmed the neuroprotective effect of rosemary extract. The following are the intervention effect data of different active components on nerve injury models, among which the higher the cell survival rate and cognitive function score, the more significant the neuroprotective effect:
| Active Component | Experimental Model | Intervention Concentration | Core Detection Index | Effect Data |
| Rosmarinic Acid | Aβ-induced nerve cell injury model | 50μmol/L | Nerve cell survival rate | Increased from 32.7% to 78.2% |
| Carnosic Acid | Alzheimer’s disease mouse model | 20mg/kg·d (gavage) | Cognitive function score in water maze test | Increased from 45.3 points to 72.6 points (full score 100 points) |
| Carnosol | Rat model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury | 15mg/kg (intraperitoneal injection) | Proportion of cerebral infarction volume | Reduced from 28.5% to 12.3% |
| Mixed Extract | Aging-related cognitive impairment mouse model | 50mg/kg·d (dietary addition) | Acetylcholine content (neurotransmitter) in hippocampus | Increased by 63.4% |
3.3 Advantage Comparison with Traditional Neuroprotective Agents
Compared with clinically commonly used cholinesterase inhibitors (such as donepezil), rosemary extract has significant advantages: first, it has a wider range of action targets, which not only improves the level of neurotransmitters, but also protects nerve cells from multiple dimensions such as anti-inflammation and anti-oxidation; second, it has fewer side effects, and long-term intervention will not cause adverse reactions such as nausea and insomnia; third, it has natural sources and relatively low cost, which is more suitable as a potential substance for daily health care and disease prevention.
4. Application Prospects and Existing Challenges
4.1 Potential Application Fields
Based on its clear anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects, rosemary extract has shown application potential in multiple fields: in the pharmaceutical field, it can be used as an auxiliary therapeutic drug component for neurodegenerative diseases (such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease) or for the development of anti-inflammatory external preparations; in the functional food field, it can be added to health foods to improve the cognitive function of the elderly and relieve discomfort related to chronic inflammation; in the daily chemical field, skin care products containing rosemary extract can reduce skin sensitivity, redness and swelling through anti-inflammatory effects.
4.2 Challenges in the Industrialization Process
Although the biological activity of rosemary extract has been fully confirmed, there are still many bottlenecks in industrial application: first, the problem of standardized extraction of active components. The content of active components in rosemary raw materials from different producing areas and harvesting seasons varies greatly, which affects the quality stability of products; second, the bioavailability needs to be improved. Some fat-soluble components (such as carnosic acid) have low absorption efficiency in the body, which needs to be optimized through preparation technologies (such as nano-encapsulation); third, clinical research is not sufficient. At present, most studies are still in the animal experiment stage, and the lack of large-scale human clinical trial data limits the full exploration of its medicinal value.
5. Conclusion
Rosemary extract shows unique advantages and great application potential in the fields of anti-inflammation and neuroprotection due to its rich active components. Its mode of action of regulating inflammatory response in multiple dimensions and protecting nerve cells through multiple pathways provides a new idea for the prevention and treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases and neurodegenerative diseases. In the future, with the standardization of extraction processes, the innovation of preparation technologies and the deepening of clinical research, rosemary extract is expected to break through the existing bottlenecks and realize industrial application in the fields of medicine, health care and daily chemicals, providing a natural and safe solution for human health.

